The Science of Reading (SoR) is a hot topic right now! As you dive into your journey, you may find yourself overwhelmed by all of the Science of Reading terms you encounter. Have no fear! Read on for 10 important Science of Reading terms you need to know.
Science of Reading Terms: Breaking down words
A single word can be broken into parts based on several different criteria. How do we know where to separate words into syllables, morphemes, and graphemes? Let’s explore!
What is a syllable?

A syllable is a word or part of a word that is organized around a vowel. It may or may not have consonants before or after the vowel. It is often described as the rhythmic part of a word or “beat”, pronounced by opening the mouth. Programs aligned with the Science of Reading teach students 6 or 7 different syllable types:
- Closed
- Open
- VCe (“Magic E” or “Silent E”)
- Consonant -le
- R-Controlled
- Vowel Team
- Diphthong (sometimes included in the “vowel team” syllable type.)
What is a morpheme?

The Science of Reading describes a morpheme as the smallest unit of meaning in a language. Morphemes can refer to the spoken or printed representation of a root, base word, suffix, or prefix. Adding or deleting morphemes changes the meaning– and often the part of speech– of a word. Since morphemes are related to meaning and not sound, they are not necessarily divided in the same way as syllables.
What is a phoneme?

A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound in a spoken language. Phonemes are all about the sound you hear when listening and produce when speaking. They are not connected to print, so any “interaction” you have with a phoneme could take place with your eyes closed. Being able to hear slight differences in phonemes helps us distinguish between similar-sounding words, like “cat” and “cut.”
What is a grapheme?
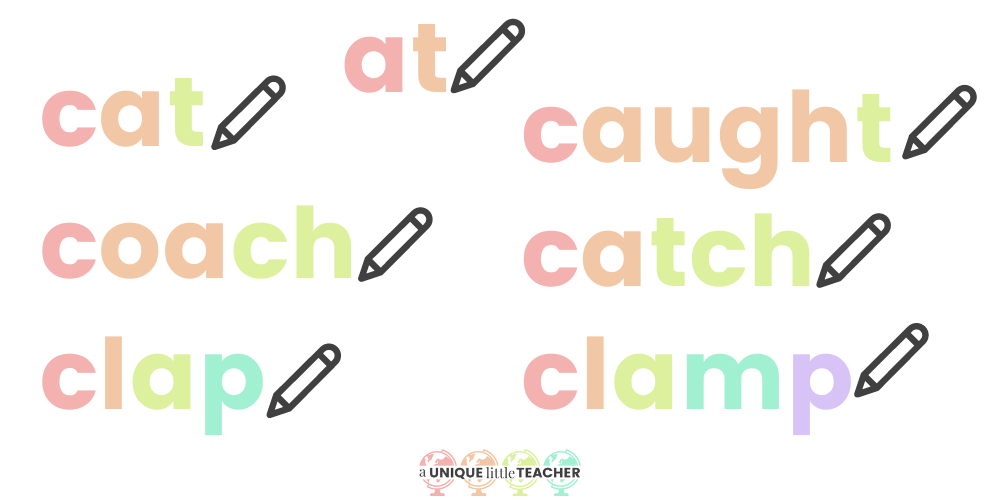
A grapheme is the printed representation of a phoneme. Graphemes are the symbols we use to read and write a language. Graphemes in English can be made up of anywhere from 1-4 letters. Teachers looking to align their instruction with the Science of Reading often find it helpful to display common graphemes in their classroom on a Grapheme Wall.
What is a phonogram?

Phonograms, like graphemes, are the printed representation of speech sounds. Phonograms include graphemes– spellings of a single sound– but can also refer to spellings of word “chunks,” like welded sounds or rimes. Instruction aligned with the Science of Reading uses phonogram cards to introduce new spellings to students and to practice learned phonograms regularly during visual and blending drills.
Science of Reading Terms: Categorizing Letters
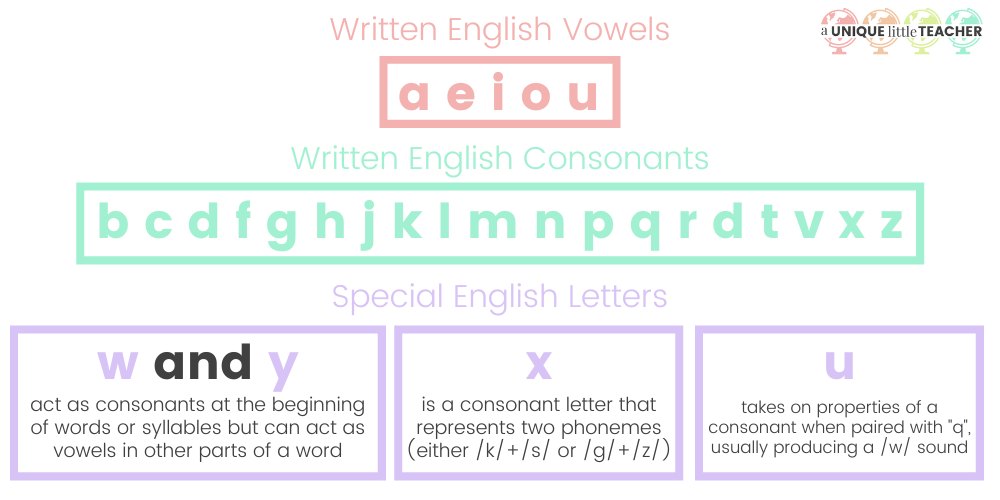
The written English language contains 26 letters of the alphabet. Some of these letters are consonants, some are vowels, and others can serve as both.
What is a consonant?
In oral language, consonants represent various types of restrictions of airflow when producing words. This restriction is created by the position of your lips, tongue, and teeth as you speak.
In written English, the consonants are b, c, d, f, g, h, j, k, l, m, n, p, q, r, s, t, v, x, and z. The letters “w” and “y” can also act as consonants at the beginning of a syllable or word (as in “wind” and “yes”).
There are more spoken consonant sounds than there are written consonants. For example, the consonant phoneme /zh/ (as in “collision”) does not have an English letter that represents it. On the other hand, the written digraph “th” is used to represent two different spoken consonant sounds (voiced and unvoiced).
What is a vowel?
In oral language, a vowel refers to sounds we make within words when air goes through our vocal cords without much restriction (compared to consonants, which involve restriction of air flow). Science of Reading practitioners often describe vowels as sounds you can “sing” because you can produce them continuously until you run out of air.
In written language, the vowels in English are a, e, i, o, and u. The letters “w” and “y” can act as vowels in the middle and end of words (as in “cow” and “any”). There are far more oral vowels than written vowels.
Science of Reading Terms: Skills and Instruction
What is phonological awareness?
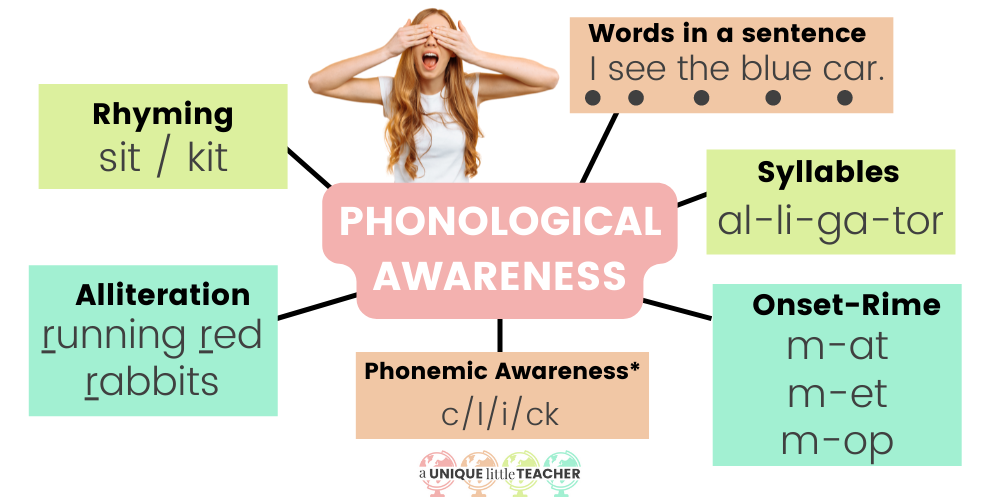
Resources based on the Science of Reading often refer to phonological awareness as the “umbrella term” that includes all the different levels of awareness of spoken language. This includes:
- Word-level awareness / understanding word boundaries
- Syllable awareness
- Rhyming skills
- Understanding of onset-rime units
- Alliteration skills
- Phonemic awareness (which we’ll talk about next)
Phonological awareness skills involve identifying and manipulating (adding/deleting/changing) these various levels of spoken language. Phonological awareness is not tied to printed language, so experts describe these skills as those that can be “done in the dark.”
What is phonemic awareness?
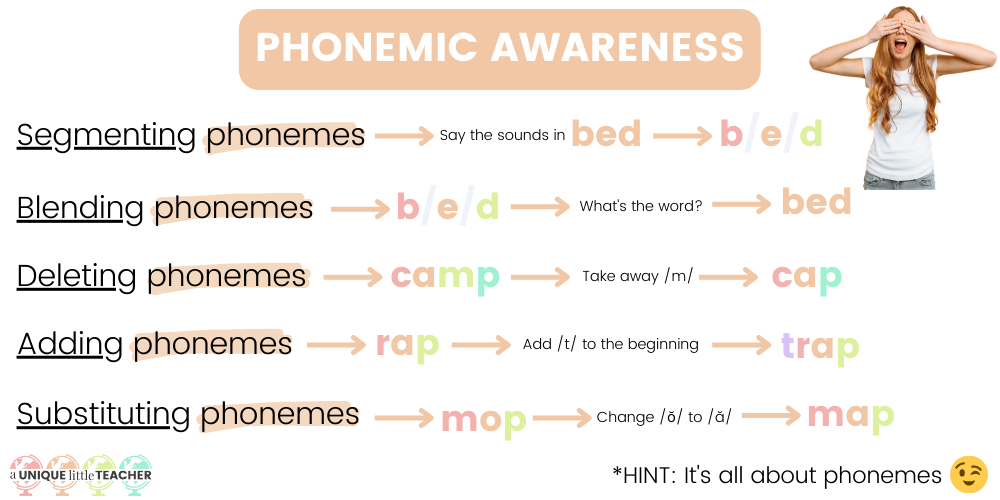
Like phonological awareness, phonemic awareness is a completely auditory skill. It does not involve printed language, so you can practice these skills with your eyes closed. Phonemic awareness is a sub-skill of phonological awareness and refers to a person’s ability to identify and manipulate the phonemes within a single word. Specific phonemic awareness skills include:
- Segmenting phonemes
- Blending phonemes
- Deleting phonemes
- Adding phonemes
- Substituting phonemes
Starting to notice a pattern here? 😅
What is phonics?
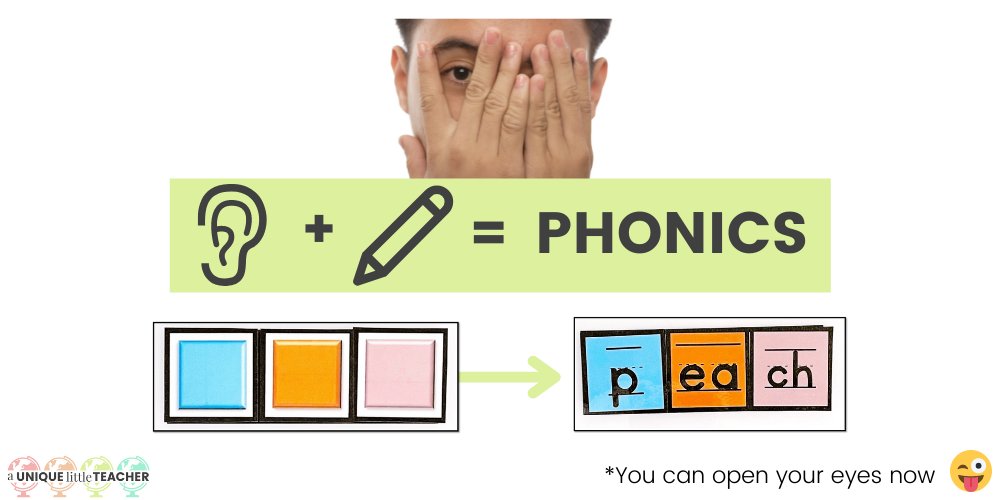
Unlike phonological and phonemic awareness, phonics connects printed symbols (letters/graphemes) to the spoken sounds they represent. Phonics involves hearing sounds and translating those sounds to symbols, as well as reading symbols and translating them to sounds. Science of Reading experts refer to these skills as “encoding” and “decoding,” respectively.
Ready to put these Science of Reading Terms to use?
Now that you’re an expert on these Science of Reading terms, use what you’ve learned to continue implementing structured literacy practices. The FREEBIE below shows you all of the 46 phonemes in the English language, the graphemes that can represent them, and a keyword (or several) for each phoneme-grapheme correspondence.
Sign up below to get your FREE master list of keywords for the phonemes and graphemes of English! You will also be added to our email community and receive free resources & teaching tips every month.






